라즈베리 파이 버튼 디바운스
버튼이 눌리거나 해제되거나 스위치가 전환될 때, 초보자들은 종종 상태가 단순히 LOW에서 HIGH로, 혹은 HIGH에서 LOW로 변경된다고 생각합니다. 실제로는 그렇지 않습니다. 기계적 및 물리적 특성 때문에 버튼(또는 스위치)의 상태는 LOW와 HIGH 사이에서 여러 번 전환될 수 있습니다. 이러한 현상을 채터링이라고 합니다. 채터링은 한 번의 누름이 여러 번의 누름으로 인식되어 특정 응용 프로그램에서 오작동을 초래할 수 있습니다.
이 문제를 방지하는 방법은 디바운싱(debouncing) 또는 디바운스(debounce)라고 합니다. 이 튜토리얼은 Raspberry Pi와 버튼을 사용할 때 이를 수행하는 방법을 알려줍니다. 우리는 아래 단계들을 통해 배울 것입니다:
버튼 디바운싱이 없는 Raspberry Pi 코드.
버튼 디바운싱이 적용된 Raspberry Pi 코드.
여러 버튼에 디바운싱이 적용된 Raspberry Pi 코드.
| 1 | × | 라즈베리 파이 5 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | 캡이 있는 버튼 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | 버튼 키트 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | 패널 장착 푸시 버튼 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | 푸시 버튼 모듈 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | 브레드보드 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | 점퍼케이블 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | (추천) 라즈베리 파이용 스크루 터미널 블록 쉴드 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | (추천) 라즈베리 파이 프로토타이핑 베이스 플레이트 & 브레드보드 키트 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | (추천) 라즈베리 파이용 HDMI 터치 스크린 모니터 | 아마존 | |
공개: 이 포스팅 에 제공된 일부 링크는 아마존 제휴 링크입니다. 이 포스팅은 쿠팡 파트너스 활동의 일환으로, 이에 따른 일정액의 수수료를 제공받습니다.
버튼의 핀 배치를 포함하여 버튼에 익숙하지 않고 작동 방식 및 프로그래밍 방법을 모르신다면 다음 튜토리얼을 통해 더 많은 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다.
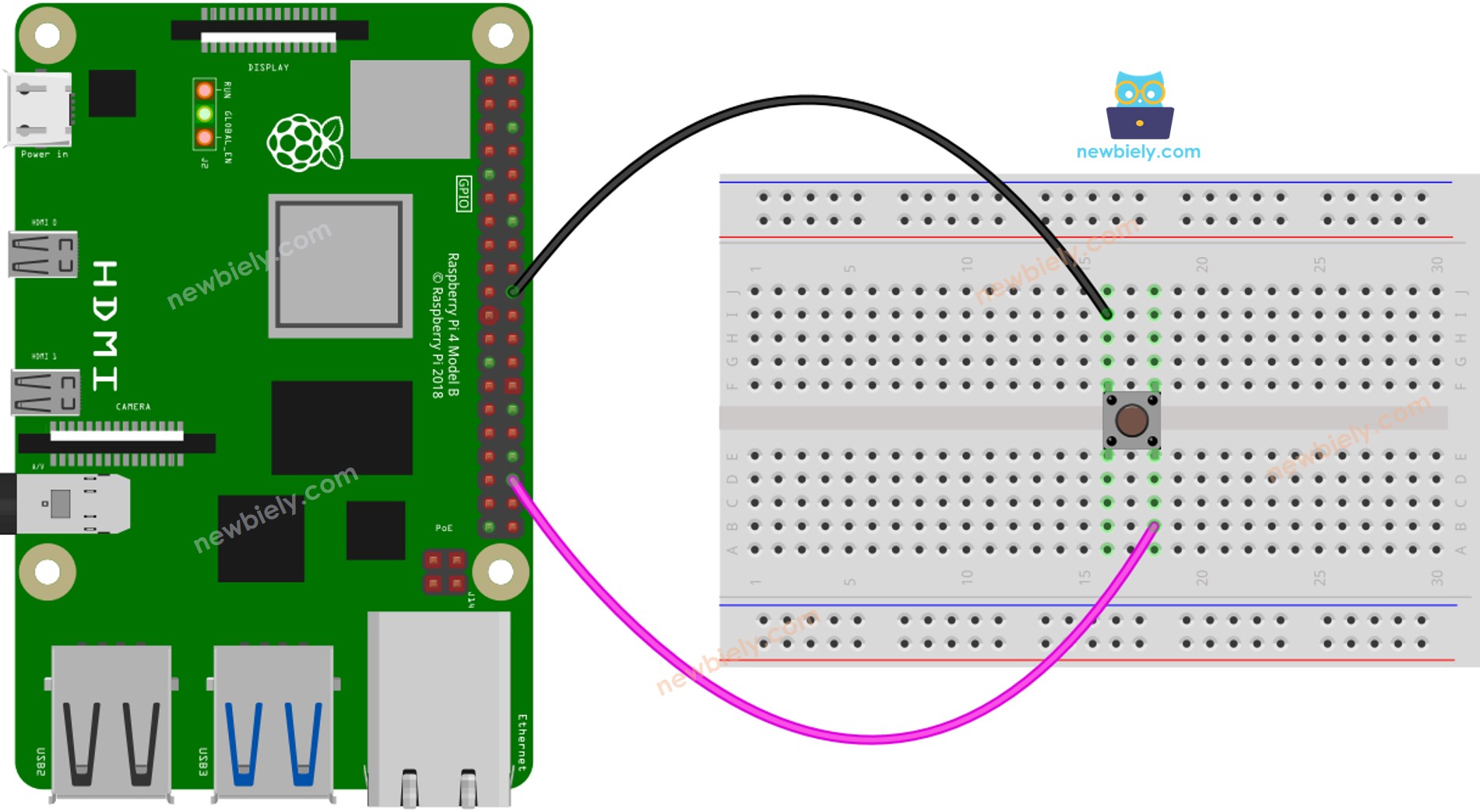
이 이미지는 Fritzing을 사용하여 만들어졌습니다. 이미지를 확대하려면 클릭하세요.
Raspberry Pi 코드에 디바운스를 적용한 경우와 적용하지 않은 경우의 차이점과 각각의 동작 방식에 대해 살펴봅시다.
디바운싱을 이해하기 전에, 디바운싱 없이 작성된 코드를 보고 그 동작을 관찰하세요.
Raspberry Pi에 Raspbian 또는 다른 Raspberry Pi 호환 운영 체제가 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요.
Raspberry Pi가 PC와 동일한 로컬 네트워크에 연결되어 있는지 확인하세요.
라이브러리 설치가 필요한 경우 Raspberry Pi가 인터넷에 연결되어 있는지 확인하세요.
RPi.GPIO 라이브러리가 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요. 그렇지 않은 경우, 다음 명령어를 사용하여 설치하세요:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-rpi.gpio
/*
* 이 라즈베리 파이 코드는 newbiely.kr 에서 개발되었습니다
* 이 라즈베리 파이 코드는 어떠한 제한 없이 공개 사용을 위해 제공됩니다.
* 상세한 지침 및 연결도에 대해서는 다음을 방문하세요:
* https://newbiely.kr/tutorials/raspberry-pi/raspberry-pi-button-debounce
*/
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
BUTTON_PIN = 16
GPIO.setup(BUTTON_PIN, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
button_state = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN)
try:
while True:
current_state = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN)
if current_state != button_state:
if current_state == GPIO.HIGH:
print("Button released")
else:
print("Button pressed")
button_state = current_state
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
GPIO.cleanup()
python3 button_without_debounce.py
스크립트는 터미널에서 Ctrl + C를 누를 때까지 무한 루프로 계속 실행됩니다.
버튼을 몇 초간 눌렀다가 놓으세요.
터미널에서 결과를 확인하세요.
Button pressed
Button pressed
Button pressed
Button released
Button released
때때로 버튼을 한 번만 눌렀다 놓았을 때도 라즈베리 파이는 이를 여러 번 눌렀다 놓은 것으로 인식합니다. 이것이 튜토리얼의 시작 부분에서 언급된 채터링 현상입니다. 다음 부분에서 이를 해결하는 방법을 알아보겠습니다.
/*
* 이 라즈베리 파이 코드는 newbiely.kr 에서 개발되었습니다
* 이 라즈베리 파이 코드는 어떠한 제한 없이 공개 사용을 위해 제공됩니다.
* 상세한 지침 및 연결도에 대해서는 다음을 방문하세요:
* https://newbiely.kr/tutorials/raspberry-pi/raspberry-pi-button-debounce
*/
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
BUTTON_PIN = 16
DEBOUNCE_TIME_MS = 200
GPIO.setup(BUTTON_PIN, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
button_state = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN)
prev_button_state = button_state
def button_callback(channel):
global button_state
button_state = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN)
GPIO.add_event_detect(BUTTON_PIN, GPIO.BOTH, callback=button_callback, bouncetime=DEBOUNCE_TIME_MS)
try:
while True:
if button_state != prev_button_state:
if button_state == GPIO.HIGH:
print("Button released")
else:
print("Button pressed")
prev_button_state = button_state
except KeyboardInterrupt:
GPIO.cleanup()
python3 button_debounce.py
버튼을 몇 초 동안 누르고 있다가 놓으세요.
결과를 확인하려면 터미널을 확인하세요.
Button pressed
Button released
보시다시피 버튼을 한 번만 눌렀다가 뗐습니다. 라즈베리 파이는 이를 단일 누름 및 뗌으로 감지하여 불필요한 잡음을 제거합니다.
/*
* 이 라즈베리 파이 코드는 newbiely.kr 에서 개발되었습니다
* 이 라즈베리 파이 코드는 어떠한 제한 없이 공개 사용을 위해 제공됩니다.
* 상세한 지침 및 연결도에 대해서는 다음을 방문하세요:
* https://newbiely.kr/tutorials/raspberry-pi/raspberry-pi-button-debounce
*/
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
BUTTON_PIN_1 = 14
BUTTON_PIN_2 = 15
BUTTON_PIN_3 = 18
DEBOUNCE_TIME_MS = 200
GPIO.setup(BUTTON_PIN_1, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(BUTTON_PIN_2, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(BUTTON_PIN_3, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
button_state_1 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN_1)
button_state_2 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN_2)
button_state_3 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN_3)
prev_button_state_1 = button_state_1
prev_button_state_2 = button_state_2
prev_button_state_3 = button_state_3
def button_callback_1(channel):
global button_state_1
button_state_1 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN_1)
def button_callback_2(channel):
global button_state_2
button_state_2 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN_2)
def button_callback_3(channel):
global button_state_3
button_state_3 = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN_3)
GPIO.add_event_detect(BUTTON_PIN_1, GPIO.BOTH, callback=button_callback_1, bouncetime=DEBOUNCE_TIME_MS)
GPIO.add_event_detect(BUTTON_PIN_2, GPIO.BOTH, callback=button_callback_2, bouncetime=DEBOUNCE_TIME_MS)
GPIO.add_event_detect(BUTTON_PIN_3, GPIO.BOTH, callback=button_callback_3, bouncetime=DEBOUNCE_TIME_MS)
try:
while True:
if button_state_1 != prev_button_state_1:
if button_state_1 == GPIO.HIGH:
print("Button 1 released")
else:
print("Button 1 pressed")
prev_button_state_1 = button_state_1
if button_state_2 != prev_button_state_2:
if button_state_2 == GPIO.HIGH:
print("Button 2 released")
else:
print("Button 2 pressed")
prev_button_state_2 = button_state_2
if button_state_3 != prev_button_state_3:
if button_state_3 == GPIO.HIGH:
print("Button 3 released")
else:
print("Button 3 pressed")
prev_button_state_3 = button_state_3
except KeyboardInterrupt:
GPIO.cleanup()
코드에 언급된 배선을 보여주는 다이어그램:
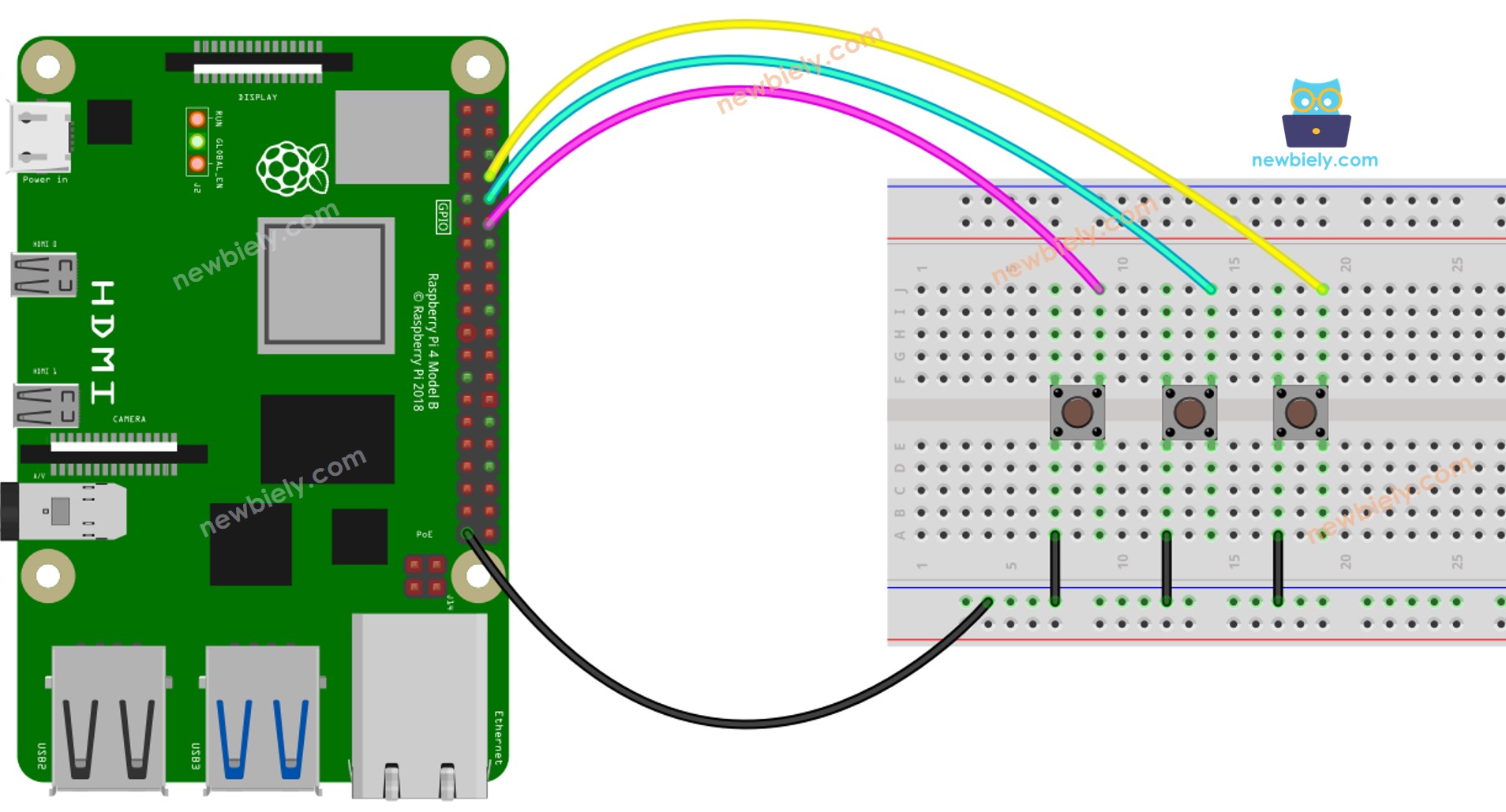
이 이미지는 Fritzing을 사용하여 만들어졌습니다. 이미지를 확대하려면 클릭하세요.
배선 구성을 간단하고 체계적으로 만들기 위해, Raspberry Pi용 스크루 터미널 블록 실드 사용을 권장합니다. 이 실드는 아래와 같이 더욱 안정적이고 관리하기 쉬운 연결을 제공합니다:
비디오 제작은 시간이 많이 걸리는 작업입니다. 비디오 튜토리얼이 학습에 도움이 되었다면, YouTube 채널 을 구독하여 알려 주시기 바랍니다. 비디오에 대한 높은 수요가 있다면, 비디오를 만들기 위해 노력하겠습니다.