ESP8266 RTC: ESP8266 RTC
이 튜토리얼은 ESP8266을 사용하여 RTC 모듈에서 날짜와 시간을 읽는 방법을 안내합니다. 자세히, 우리는 배울 것입니다:
DS3231 실시간 시계 모듈을 ESP8266에 연결하는 방법.
ESP8266을 프로그래밍하여 DS3231 RTC 모듈에서 날짜와 시간(초, 분, 시, 요일, 월의 일수, 월, 연도)을 읽는 방법.
ESP8266을 프로그래밍하여 매일 일정을 생성하는 방법.
ESP8266을 프로그래밍하여 매주 일정을 생성하는 방법.
ESP8266을 프로그래밍하여 특정 날짜에 일정을 생성하는 방법.
| 1 | × | ESP8266 NodeMCU | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | USB 케이블 타입-A to 타입-C (USB-A PC용) | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | USB 케이블 타입-C to 타입-C (USB-C PC용) | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | DS3231 실시간 클록(RTC) 모듈 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | CR2032 배터리 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | 점퍼케이블 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | (추천) ESP8266용 스크루 터미널 확장 보드 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
| 1 | × | (추천) ESP8266 Type-C용 전원 분배기 | 쿠팡 | 아마존 | |
공개: 이 포스팅 에 제공된 일부 링크는 아마존 제휴 링크입니다. 이 포스팅은 쿠팡 파트너스 활동의 일환으로, 이에 따른 일정액의 수수료를 제공받습니다.
ESP8266에는 millis() 및 micros()와 같이 시간과 관련된 특정 함수가 있습니다. 그러나 이 함수들은 시간(초, 분, 시, 일, 날짜, 월, 년)을 제공하지 않습니다. 이 정보를 얻으려면 DS3231 또는 DS1370과 같은 실시간 시계(RTC) 모듈을 사용해야 합니다. DS3231 모듈은 DS1370보다 더 높은 정밀도를 가지고 있습니다. 보다 자세한 정보는 DS3231 vs DS1307을 참조하세요.
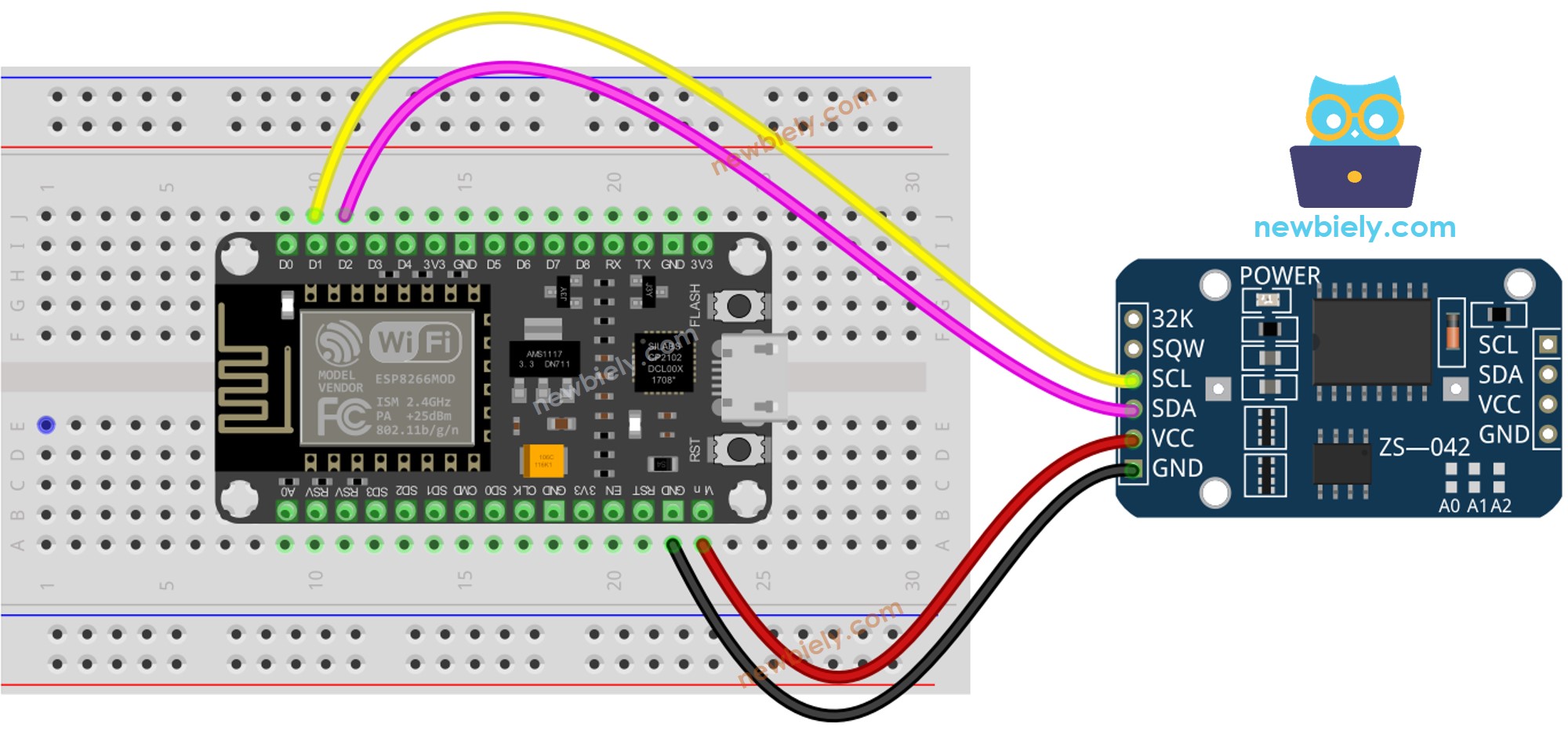
실시간 시계 DS3231 모듈에는 10개의 핀이 있습니다:
32K: 이 핀은 안정적이고 정확한 기준 클록을 제공합니다.
SQW: 이 핀은 1Hz, 4kHz, 8kHz 또는 32kHz에서 사각파를 생성하며 프로그래밍을 통해 관리할 수 있습니다. 또한 다양한 시간 의존적 애플리케이션에서 알람 인터럽트로 사용될 수 있습니다.
SCL: 이것은 I2C 인터페이스를 위한 직렬 클록 핀입니다.
SDA: 이것은 I2C 인터페이스를 위한 직렬 데이터 핀입니다.
VCC: 이 핀은 모듈에 전력을 공급합니다. 3.3V에서 5.5V 사이일 수 있습니다.
GND: 이것은 지상 핀입니다.
정상 작동을 위해서는 VCC, GND, SDA, SCL 이라는 네 개의 핀이 필요합니다.
DS3231 모듈에는 CR2032 배터리가 삽입되면 주전원이 꺼져 있을 때에도 모듈의 시간을 계속 유지시켜 주는 배터리 홀더가 있습니다. 배터리가 없는 경우, 주전원이 끊어지면 시간 정보가 소실되어 다시 설정해야 합니다.
이 이미지는 Fritzing을 사용하여 만들어졌습니다. 이미지를 확대하려면 클릭하세요.
ESP8266 핀배열 및 ESP8266 전원을 켜는 방법에 대해 더 많이 보십시오.
| DS3231 RTC Module | ESP8266 |
|---|
| Vin | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SDA | GPIO4 |
| SCL | GPIO5 |
라이브러리를 포함하세요.
RTC 객체를 생성하십시오.
RTC 설정 과정을 시작하세요.
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("RTC를 찾을 수 없습니다");
while (1);
}
스케치가 처음 컴파일될 때 컴퓨터의 날짜와 시간으로 RTC를 설정하세요.
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
RTC 모듈에서 날짜와 시간 데이터를 검색합니다.
DateTime now = rtc.now();
Serial.print("Date & Time: ");
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(now.dayOfTheWeek());
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(now.second(), DEC);
#include <RTClib.h>
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
Serial.flush();
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
Serial.print("Date & Time: ");
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[now.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(now.second(), DEC);
delay(1000);
}
Arduino IDE에서 ESP8266을 시작하는 방법은 다음 단계를 따르세요:
다이어그램에 표시된 대로 구성 요소를 배선하세요.
USB 케이블을 사용하여 ESP8266 보드를 컴퓨터에 연결하세요.
컴퓨터에서 Arduino IDE를 엽니다.
올바른 ESP8266 보드를 선택하세요. 예를 들어, NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module) 및 해당 COM 포트를 선택합니다.
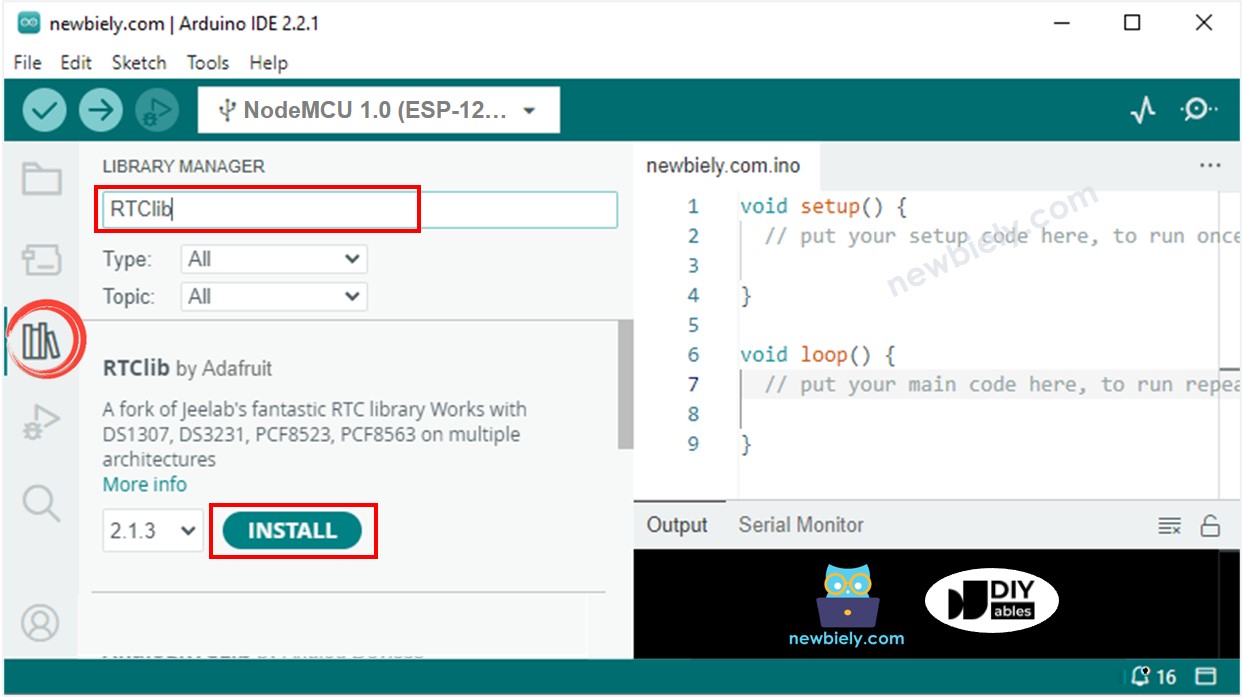
Arduino IDE의 왼쪽 바에 있는 Libraries 아이콘을 클릭하세요.
“RTClib”을 검색하여 Adafruit의 RTC 라이브러리를 찾으세요.
RTC 라이브러리를 설치하려면 Install 버튼을 누르세요.
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:35
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:36
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:37
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:38
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:39
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:40
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:41
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:42
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:43
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 11:27:44
#include <RTClib.h>
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_START_HH = 13;
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_START_MM = 50;
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_END_HH = 14;
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_END_MM = 10;
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
if (now.hour() >= DAILY_EVENT_START_HH &&
now.minute() >= DAILY_EVENT_START_MM &&
now.hour() < DAILY_EVENT_END_HH &&
now.minute() < DAILY_EVENT_END_MM) {
Serial.println("It is on scheduled time");
} else {
Serial.println("It is NOT on scheduled time");
}
printTime(now);
}
void printTime(DateTime time) {
Serial.print("TIME: ");
Serial.print(time.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[time.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(time.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(time.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(time.second(), DEC);
}
#include <RTClib.h>
#define SUNDAY 0
#define MONDAY 1
#define TUESDAY 2
#define WEDNESDAY 3
#define THURSDAY 4
#define FRIDAY 5
#define SATURDAY 6
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_DAY = MONDAY;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_START_HH = 13;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_START_MM = 50;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_END_HH = 14;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_END_MM = 10;
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
if (now.dayOfTheWeek() == WEEKLY_EVENT_DAY &&
now.hour() >= WEEKLY_EVENT_START_HH &&
now.minute() >= WEEKLY_EVENT_START_MM &&
now.hour() < WEEKLY_EVENT_END_HH &&
now.minute() < WEEKLY_EVENT_END_MM) {
Serial.println("It is on scheduled time");
} else {
Serial.println("It is NOT on scheduled time");
}
printTime(now);
}
void printTime(DateTime time) {
Serial.print("TIME: ");
Serial.print(time.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[time.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(time.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(time.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(time.second(), DEC);
}
#include <RTClib.h>
#define SUNDAY 0
#define MONDAY 1
#define TUESDAY 2
#define WEDNESDAY 3
#define THURSDAY 4
#define FRIDAY 5
#define SATURDAY 6
#define JANUARY 1
#define FEBRUARY 2
#define MARCH 3
#define APRIL 4
#define MAY 5
#define JUNE 6
#define JULY 7
#define AUGUST 8
#define SEPTEMBER 9
#define OCTOBER 10
#define NOVEMBER 11
#define DECEMBER 12
DateTime EVENT_START(2021, AUGUST, 15, 13, 50);
DateTime EVENT_END(2021, SEPTEMBER, 29, 14, 10);
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
Serial.flush();
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
if (now.secondstime() >= EVENT_START.secondstime() &&
now.secondstime() < EVENT_END.secondstime()) {
Serial.println("It is on scheduled time");
} else {
Serial.println("It is NOT on scheduled time");
}
printTime(now);
}
void printTime(DateTime time) {
Serial.print("TIME: ");
Serial.print(time.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[time.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(time.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(time.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(time.second(), DEC);
}
비디오 제작은 시간이 많이 걸리는 작업입니다. 비디오 튜토리얼이 학습에 도움이 되었다면, YouTube 채널 을 구독하여 알려 주시기 바랍니다. 비디오에 대한 높은 수요가 있다면, 비디오를 만들기 위해 노력하겠습니다.